Learning how to add bots to ChatGPT can save time, boost work speed, and help businesses grow fast. This simple skill turns ChatGPT into a smart, automated helper.
Everyone’s missing this trick, so don’t be left behind. Adding a ChatGPT bot is more than a tech upgrade, it is a way to work smarter. In this context, a “bot” can mean a custom GPT, an automation agent, or a tool powered by the ChatGPT API. These bots can run tasks, give answers, and link with your favorite apps.
This guide is not theory. It is a clear, step-by-step plan that shows how to build, connect, and use bots in real life. You will learn how to set them up, where to use them, and how to avoid common mistakes.
What Exactly Does Adding Bots to ChatGPT Mean?

Adding bots to ChatGPT means turning it into an automated system that works for you. Bots can be custom GPTs or connected tools that handle real tasks with speed and accuracy.
When people talk about “adding bots” to ChatGPT, they often mean creating custom GPTs through the GPT Builder or linking ChatGPT to apps and tools using the ChatGPT API. A bot can answer questions, manage workflows, or automate small jobs.
There are three main types of bots. First, built-in GPTs that you can create inside ChatGPT. Second, external bots that connect to websites or apps through API calls. Third, hybrid bots that mix both. Each type serves a different need, from personal tasks to full business automation.
These bots act like smart assistants. They run in the background, take commands, and help you save time. That is why many companies and creators use them to grow fast.
2.1 What is a “bot” in the ChatGPT ecosystem?
A bot in the ChatGPT world is a tool or program that uses GPT models to respond, act, or connect with other apps automatically.
You can build a simple ChatGPT bot inside OpenAI’s platform with the GPT Builder. This lets you create a custom GPT that follows your rules and gives specific answers. Or, you can make API-driven bots. These connect ChatGPT to apps, websites, or business tools like CRM systems.
The difference is simple. Built-in GPTs live inside ChatGPT. External bots work on other platforms and use the ChatGPT API. Hybrid bots blend both. This structure gives users more control, speed, and real-time power.
2.2 Why do people build bots for ChatGPT?
People build bots to automate boring tasks, speed up workflows, and make their business or personal work easier.
A GPT builder bot can reply to customers in real time. A ChatGPT API bot can handle reports or update data in seconds. These bots give a strong edge to early adopters. Businesses use them to scale support, cut costs, and work smarter.
Even students or creators can use these bots to collect data, draft emails, or manage schedules. By building your own bot, you get a smart helper that never sleeps.
2.3 What the common guides miss
Most guides skip real business needs, database links, and security steps. That is why many bots don’t work well in real use.
Many tutorials only show the setup. They focus on prompts or API keys. But they don’t explain how to build data pipelines, secure the bot, or connect it with real-time data.
This is the gap we’ll fill in this guide. You will learn not just how to build a bot, but how to make it strong, safe, and useful for real work. We’ll cover integration workflow, chatbot platform links, and ethical steps so your bot is ready for real-world use.
Prerequisites: What You’ll Need Before You Start
To add bots to ChatGPT, you need the right account, a clear goal, a solid data plan, and the right tools. With these ready, your build becomes fast and smooth.
Before you build your ChatGPT bot, you must set a strong base. This step saves time later and makes your bot work better. You need access to ChatGPT or its API, a clear idea of what your bot will do, and a small tech setup. Once this is in place, the rest becomes easy.
3.1 Technical & Account Requirements
You need a paid ChatGPT account for custom GPTs or API access for more control. A bit of basic tech knowledge helps a lot.
Start with the basics. A ChatGPT Plus or API plan gives you access to GPT-4 and custom GPT features. You’ll also need your API key if you want to build bots outside ChatGPT.
It helps to understand simple prompts, keys, and maybe some basic programming or no-code tools. Even a little practice can make setup easier.
3.2 Define Your Goal: What Will Your Bot Do?
Decide the purpose of your bot before you build it. Clear goals make the setup focused and easy.
Ask yourself what you want the bot to do. It can give customer support, act as an internal assistant, or handle personal tasks like scheduling. Map out your main workflows, the kind of users who will interact, and the outcomes you want.
This step will shape your prompts, your tools, and how your bot connects with data later.
3.3 Data & Database Prerequisites
If your bot needs real-time updates, connect it to a database. This keeps it smart and fresh.
Bots become more powerful when they use real-time databases. You can use Firestore, MongoDB, or PostgreSQL to pull updates, logs, or reports. If your project is complex, you can add a vector database for advanced retrieval using embeddings.
Think about privacy and data freshness too. Old data can make bots less useful. A clear data plan avoids problems later.
3.4 Tooling List (High-Level)You need the right mix of tools for building, storing, connecting, and monitoring your bot.
Here’s a simple list to get started:
- ChatGPT API or GPT Builder interface for bot creation.
- Real-time database or vector store for data (Firestore, MongoDB, PostgreSQL).
- A webhook server or no-code platform like Zapier or n8n for linking everything.
- Monitoring and logging tools to keep track of performance and errors.
Before you start, make sure you have all these tools ready. This will make learning how to add bots to ChatGPT much smoother. These tools give your bot structure and support. With them, your setup will stay stable and easy to grow.
Step-by-Step: How to Add Bots to ChatGPT
This is the main part of learning how to add bots to ChatGPT. Here we build, connect, and launch. Adding bots to ChatGPT is easy if you follow a clear process. First, build your bot, then link the API, connect data, add memory, deploy it, and keep it secure.
This is the most important part of your journey. Each step builds on the last. By the end of this section, you’ll know how to make a smart, working bot with or without code.
4.1 How do you build a custom GPT (no code) for ChatGPT?
Use GPT Builder inside ChatGPT to make your own bot. You can set its name, role, and behavior with no coding needed.
Open ChatGPT and go to the GPT Builder section. Click “Create.” Give your bot a name and describe what it should do. Add instructions, define its role, and upload files if needed.
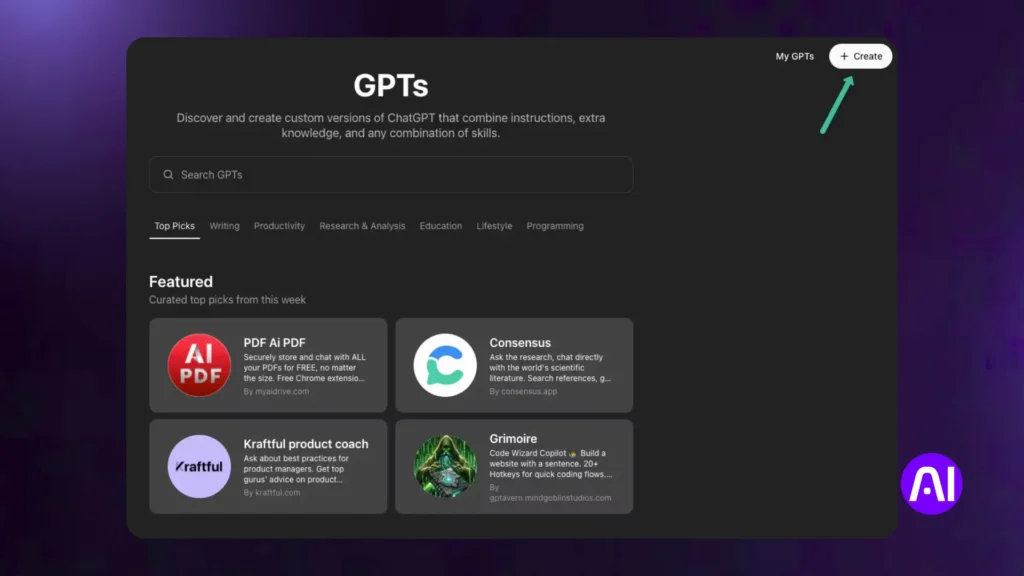
You can set fallback prompts to guide the bot when it is unsure. Then test and refine it. This is the fastest way to build a custom GPT without touching code.
4.2 How Do You Integrate the ChatGPT API Into Your Own Bot?
Integrating the ChatGPT API is one of the best ways to make your bot work outside the main platform. This gives you more control, lets you add features, and allows the bot to work on your own website or app. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you do it easily:
Step 1: Create an OpenAI Account and Get Your API Key
To use ChatGPT in your bot, you need an API key. This key connects your bot to ChatGPT’s brain.
- Go to OpenAI.
- Sign up or log in to your developer account.
- Click on your profile icon in the top-right corner.
- Select “View API Keys.”
- If you don’t have one already, click “Create new secret key.”
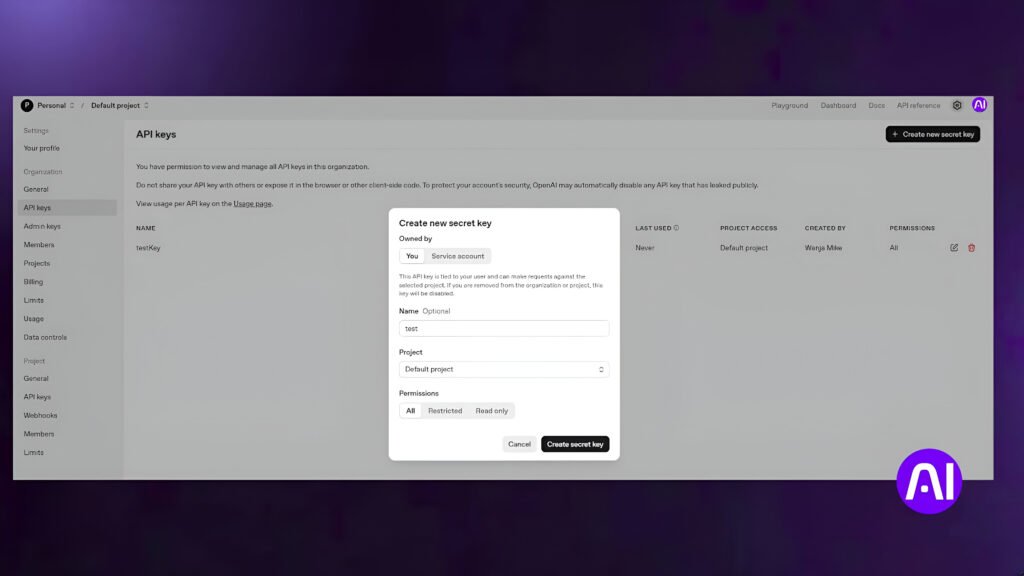
- Add a name (optional) and click Create secret key.
- Copy and save the key in a safe place, like a text file.
Tip: Don’t share this key with anyone. If someone else gets it, they can use your account.
Step 2: Choose Your Development Environment
In this step, we’ll use Python and JavaScript to create a simple ChatGPT bot that responds to a question in the command terminal.
Start by creating an empty project folder on your computer. Then, open it in your Integrated Development Environment (IDE). In this example, we’ll use Visual Studio Code because it’s free and beginner friendly, but you can use any IDE you like.
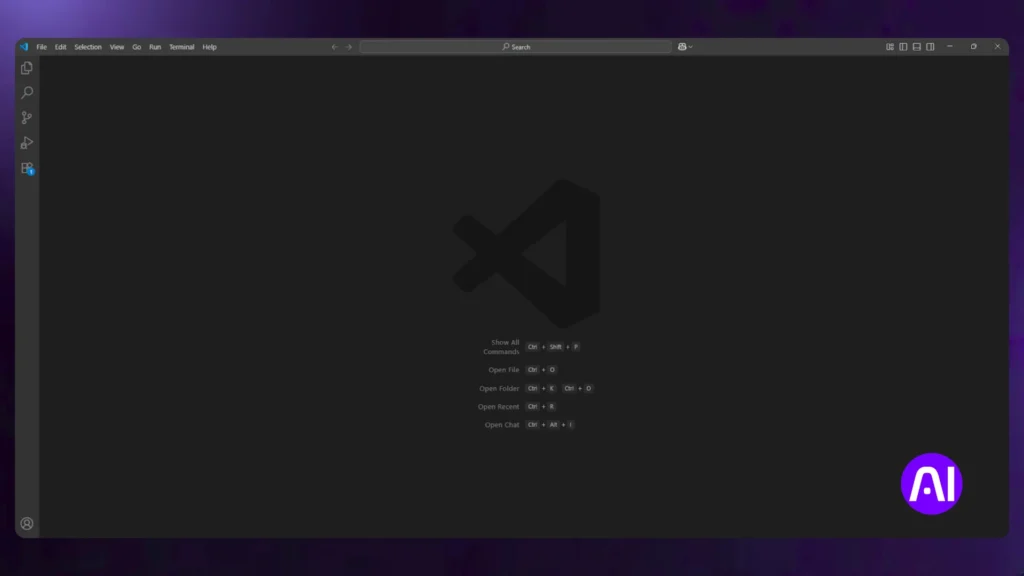
- Python (best for beginners)
- JavaScript with Node.js (great for web projects)
If you choose JavaScript:
- Download and install Node.js.
- It comes with NPM (Node Package Manager) so you can install libraries easily.
If you choose Python:
- Make sure Python is installed on your computer.
- Use pip to install required packages like openai.
This is the base environment where your bot will talk to ChatGPT through the API.
Step 3: Install the Required Libraries
For JavaScript, open your terminal or command prompt and run:
| npm install openai |
For Python, run:
| pip install openai |
This will install the official OpenAI package to help you send messages to ChatGPT.
Step 4: Connect Your API Key to the Project
In your code, you need to link your secret key.
For Python:
| import openai openai.api_key = “YOUR_API_KEY” |
For JavaScript (Node.js):
| import OpenAI from “openai”; const client = new OpenAI({ apiKey: “YOUR_API_KEY” }); |
Tip: Don’t hardcode the key in public files. Store it in a .env file or your system’s environment variables for security.
Step 5: Send Prompts and Receive Responses
Use the /v1/chat/completions endpoint to make your bot talk.
Python Example:
| response = openai.ChatCompletion.create( model=”gpt-4″, messages=[{“role”: “user”, “content”: “Hello bot!”}] ) print(response.choices[0].message[“content”]) |
JavaScript Example:
| const response = await client.chat.completions.create({ model: “gpt-4”, messages: [{ role: “user”, content: “Hello bot!” }], }); console.log(response.choices[0].message.content); |
When you run this, your bot will reply to your prompt just like ChatGPT does in the browser.
Step 6: Add Features and Automation
Once your bot works, you can make it smarter by:
- Adding buttons and triggers
- Saving user conversations
- Automating replies
- Using your bot on websites, apps, or messaging platforms
This is how most businesses and creators build custom ChatGPT bots that can run anywhere.
Pro Tip: If you want your bot to stay accurate, use streaming updates and proper error handling. Keep your prompts clean and refine them regularly to make your bot sound more natural.
4.3 How do you connect a real-time database so your bot stays updated?
Pick a database like Firestore or MongoDB, then let your bot pull live data before it answers. This keeps it accurate and fresh.
Choose your database. Set up webhooks or streaming to feed new data into your system. Before the bot responds, it queries the database and enriches the prompt. This method is called retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
With RAG, your bot always speaks with the latest data. This is perfect for real-time support, live dashboards, or tracking updates.
4.4 How do you handle conversation flow and memory?
Keep track of each chat using session tokens or a small database. This lets your bot remember what happened before.
ChatGPT uses roles like “system,” “user,” and “assistant” to keep context. You can store session data in memory or save it in a file or database for longer use.
Good memory design makes your bot feel smart and personal. It can follow up, answer related questions, and handle longer conversations smoothly.
4.5 How to deploy the bot (web, Slack, WhatsApp, internal tool)?
Choose a platform, connect your bot through webhooks or scripts, and make it live where users are.
You can deploy your ChatGPT bot on a website using an embed script. Or, connect it to Slack, WhatsApp, or Microsoft Teams through OAuth and webhooks.
For example, a Slack bot can respond to team messages in real time. A website bot can chat with visitors. Choose what fits your goal best.
4.6 How to secure, monitor and maintain your bot?
Keep your API key safe, track errors, and update your bot often. This protects users and keeps your system strong.
Never expose your API key in public code. Avoid sharing sensitive data through your bot. Watch logs to catch mistakes or weird responses early.
Plan regular updates to prompts and your database. A secure and well-maintained bot runs smoothly, protects data, and builds user trust. Once you secure and monitor it well, you’ll know exactly how to add bots to ChatGPT the right way.
Tools, Platforms & Resources Worth Knowing
When building a bot powered by ChatGPT, choosing the right tools makes or breaks the experience. From no-code solutions to advanced developer frameworks, here are the key platforms every builder should know.
5.1 What Are the Core Tools to Build ChatGPT Bots?
| Tool / Platform | Best For | Pros | Cons | Pricing Considerations |
| OpenAI API (GPT-4) | Developers & power users | Full control, advanced features, supports retrieval and streaming | Requires coding knowledge, usage costs can scale up | Pay-per-use (token-based) |
| GPT Builder Interface | Non-coders, fast prototyping | No coding required, user-friendly interface, good for demos | Limited flexibility, harder to integrate with external systems | Free for Pro users (ChatGPT Plus) |
| Zapier / n8n | Automation & workflow integration | Easy integration with hundreds of apps, drag-and-drop workflows | Limited customization for complex logic | Freemium, paid plans for more workflows |
| Vector Databases (Pinecone, Chroma, Weaviate) | Memory & knowledge storage for bots | Supports RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), great for updating context dynamically | More setup required, mostly for intermediate to advanced users | Usage-based; Pinecone has free tier |
| Real-time Databases (Firebase, MongoDB Atlas) | Real-time data sync | Keep your bot updated with live info, easy to scale | Must handle structure and security carefully | Freemium tiers available |
5.2 Which Tools Are Best for Beginners vs Advanced Users?
- Beginners / No-Code:
- GPT Builder Interface → Easiest way to create a working bot without coding.
- Zapier / n8n → Ideal for automating tasks like “if message, then respond.”
- Intermediate to Advanced:
- OpenAI API → Perfect if you want to customize prompts, conversation flow, or integrate external data.
- Vector Databases (Pinecone, Chroma) → Best when your bot needs memory and dynamic knowledge updates.
- Firebase or MongoDB Atlas → Great for storing and retrieving live user data or messages.
Pro Tip: Combine Tools for Real Power
- Use GPT Builder to prototype quickly.
- Connect Zapier to automate workflows.
- Add Pinecone or Firebase to give your bot live memory and real-time context.
Real-World Use Cases & Case Studies
Below are real examples of how companies use bots built with platforms like ChatGPT and similar large-language-model (LLM) systems to boost business performance and productivity. Written simply so it’s easy to follow.
Example: Business Internal Assistant
Use Case: A sales team uses a bot linked to their CRM to pull up the client’s history and suggest the next steps.
Case Study 1:
- User: A mid-sized tech company (via BotsCrew) implemented an internal GPT for employees.
- Challenge: The company grew rapidly, employees were overloaded, and information was scattered.
- Solution: They built a custom internal GPT that could access internal knowledge, answer employee questions, and act as an assistant.
- Takeaway: Internal bots can act as productivity assistants, reducing wasted time and helping staff find answers faster.
Example: Customer-Support Bot Powered by Real-Time Database
Use Case: An e-commerce website uses a bot that checks order status and answers questions in real time.
Case Study 2:
- User: A company automates responses to reviews using a ChatGPT-powered solution (via Auxis)
- Challenge: Replies to Google and TripAdvisor reviews were manual, slow, and laborious.
- Solution: The bot composed and posted responses in seconds (20-30 reviews and 20-40 TripAdvisor posts daily) with near-real-time turnaround.
- Takeaway: Customer-support bots linked to live data sources can scale service, keep customers happy, and free human agents for harder problems.
Each case shows real results not just theory and emphasises the value of connecting AI bots with actual data and use-cases rather than treating them as standalone chat systems.
Common Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Even the best chatbot projects can fail if key issues are ignored. Below are the most common mistakes developers make when building bots with ChatGPT and how to fix them before they become critical.
6.1 Mistake: Letting Your Bot Access Stale or Incorrect Data
When your real-time database isn’t updated, your bot may rely on outdated or wrong information, leading to inaccurate or irrelevant answers.
How to Fix It:
- Implement real-time streaming updates so the bot always has the latest data.
- Use validation checks to flag outdated entries before they’re used.
- Schedule regular database syncs or webhook triggers to refresh context.
6.2 Mistake: Forgetting User Context or Memory
Without proper session handling, the bot can’t remember past interactions, resulting in repetitive or disconnected conversations.
How to Fix It:
- Store session tokens or conversation logs temporarily.
- Create user profiles to personalize interactions.
- Define clear context windows so the bot maintains coherent dialogues.
6.3 Mistake: Exposing Sensitive or Private Data
Leaking personal or system data through a bot is a major security risk.
How to Fix It:
- Enforce role-based access controls to limit sensitive data exposure.
- Mask or sanitize data before sharing it through the bot.
- Regularly audit API usage and access logs to detect leaks early.
6.4 Mistake: Relying on Default Prompts Only
Default prompts rarely perform well in complex or edge-case scenarios.
How to Fix It:
- Use prompt engineering to refine instructions.
- Add fallback prompts for unexpected user inputs.
- A/B test different prompt structures to see what performs best.
6.5 Mistake: Ignoring Metrics and Feedback
Without feedback loops, you can’t improve your bot’s performance.
How to Fix It:
- Track usage logs and analyze conversation patterns.
- Collect user satisfaction data through feedback widgets.
- Continuously iterate based on real user behavior.
Pro Tip: Treat Your Bot Like a Living System
Chatbots are not “set and forget.” Ongoing bot maintenance, data freshness, prompt iteration, and security checks are crucial for keeping them smart, safe, and useful.
Advanced Strategies: The Trick Everybody’s Missing
Most people build a bot once and leave it as it is. That’s the mistake. The real power comes from making your bot smarter every single day.
7.1 The Trick: Real-Time Feedback Loops
The missing piece is a live feedback loop. This means linking your bot with a real-time database and trigger-based actions.
With a feedback loop, your bot updates its knowledge automatically and becomes more accurate over time.
You can feed new data into your database, trigger an update, and let the bot learn without manual input. This keeps your bot fresh, fast, and smart.
7.2 Using NLP Embeddings + Vector Search
For more context-aware answers, combine vector search, NLP embeddings, and ChatGPT prompts.
This allows your bot to find the most relevant information fast before replying.
You can store your knowledge base as embeddings. When a user asks something, the system finds the most related content using vector search, then sends that context to ChatGPT. This improves accuracy and user trust.
7.3 How to Measure, Iterate, and Scale
Your bot can’t improve without data and testing.
Track every interaction, test new prompts, and measure response quality.
Use A/B testing to compare replies, build a simple dashboard to watch performance, and set conversion goals. Over time, this tells you what works and what doesn’t.
7.4 Future Trend: GPT Bot Marketplaces
Soon, custom GPTs will become products. Developers can publish their bots to GPT marketplaces and get early user adoption.
This means you can build once and scale fast by sharing your bot with the world.
This shift will push more companies to invest in smarter, more flexible bots. Those who adopt early will lead.
7.5 Adopt a “Bot Lifecycle” Mindset
Great bots go through stages: build → deploy → monitor → refine → scale.
Continuous improvement is what separates basic bots from business-changing ones.
If you build this architecture now, you stay ahead. If you wait, others will take the lead.
Conclusion
You’ve seen how to add bots to ChatGPT from what a bot is, to what you’ll need, the step-by-step build, real world use-cases, key tools, common mistakes, and the advanced trick that gives you the edge. Now it’s time to get moving.
Pick one small bot this week. Maybe one that handles a simple task in your workflow or serves a small team. Connect a real-time database so your bot is smart and up-to‐date. Run a quick test with your team or customers and watch what happens. The trick everyone’s missing is the feedback loop, once your bot learns, you lead.
Stay updated on AI trends! For more expert tips and the latest breakthroughs, follow the AI Ashes Blog. Dive deeper into machine learning, data science, and cutting-edge AI research.
Check out this article on Master NLP Best Practices for Analyzable & Clear Data for more insight into building strong NLP systems.
FAQs
Q1: What exactly is a ChatGPT bot?
A ChatGPT bot is a tool built on the ChatGPT API or custom GPTs that can answer questions, perform tasks, or link with apps.
Q2: Do I need to code to build a custom GPT?
No. You can use the GPT Builder interface to create a custom GPT without coding. For deeper integrations you’d use API.
Q3: Is a real-time database necessary for my bot?
Only if your bot needs up-to-date data. If it answers fixed questions you might not need one.
Q4: How do I keep user context so the bot feels smart?
Store session info or user profiles and pass past conversation roles (system, user, assistant) into prompts.
Q5: What is retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and why use it?
RAG means looking up info in a database or vector store and then sending that context to ChatGPT so answers are more accurate.
Q6: How do I measure if my bot is successful?
Track metrics like response time, user satisfaction, number of human hand-offs, and conversion or task completion rate.
Q7: What are common security risks for ChatGPT bots?
Exposing API keys, leaking private data, and outdated data are key risks. Use access controls, audit logs, and data validation.
Q8: How often should I update or refine my bot’s prompts and data?
Regularly. After deployment you should monitor logs, collect feedback, fix edge-cases, and refresh knowledge base as needed.
Q9: Can I publish my custom GPT or bot to a marketplace?
Yes. Many platforms now allow publishing custom GPTs so others can use them. This can give you visibility and maybe revenue.
Q10: What is the main trick everyone seems to miss?
Building the live feedback loop: database ➝ trigger ➝ ChatGPT ➝ improvement. That makes the bot smarter over time, not just static.







